|
|||||
 |
 |
||||
| CEE Website is in "Archive" status — read the announcement | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| About CEE |
|---|
|
About CEE — Archive
Why CEE | Benefits of CEE | CEE Architecture | Community
Common Event Expression (CEE™) improves the audit process and the ability of users to effectively interpret and analyze event log and audit data. This is accomplished by defining an extensible unified event structure, which users and developers can leverage to describe, encode, and exchange their CEE Event Records.
Why CEE
Event management relies on event logs. In today’s organizations, this process involves the interpretation of many different types of events, expressed using different terminologies, and represented in a multitude of formats. The goal of CEE is to unify the event categorization, terminologies, and representation formats, while also allowing organizations to tailor event reporting to meet particular needs.
By using CEE’s common language and syntax, enterprise-wide log management, correlation, aggregation, auditing, and incident handling can be performed more efficiently and produce better results than was possible prior to CEE. Additionally, CEE allows an organization to demonstrate compliance with audit requirements (e.g., HIPAA, FISMA, SOX); detect information access policy violations; improve awareness of enterprise asset status and availability (e.g., IT, SCADA), and improve awareness of attempted intrusions and other threats.
CEE Benefits
CEE provides benefits to a broad range of users and groups, including event consumers and event producers.
End User Groups (Event Consumers)
- System Administrators — learn of impaired access, hardware failures, system abnormalities, and where to focus troubleshooting
- Security Analysts — learn of presence of cyber threats including intrusion and malware
- Help Desk — provide a higher level of service informed by improved awareness of user actions and context
- Compliance — produce targeted and detailed audit reports of user and system activity
Vendors/Developers (Event Producers)
- Software Engineers — ease of integration into existing enterprise architectures
- Product Managers — interoperability across product lines and platforms
- Sales — increased consumer demand for products that implement CEE
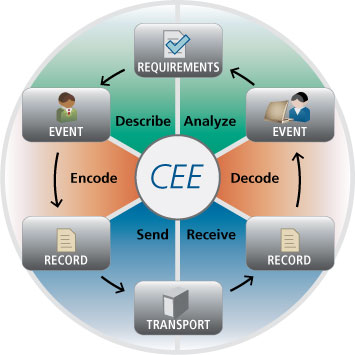
CEE standardizes the three main pieces of the Event Lifecycle:
Requirements, Events, and Records
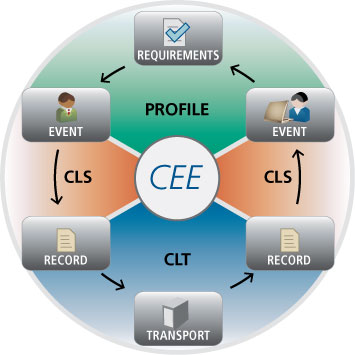
CEE Architecture
The CEE architecture focuses on the three pieces of the Event Lifecycle: Requirements, which are addressed in the CEE Profile; Events, which are represented as records using the CEE Log Syntax (CLS); and Records, which are shared via a CEE Log Transport (CLT).
Requirements
CEE Profile
The CEE Profile defines the structure of a CEE Event. This event structure includes a user-customizable CEE Event Profile definition, a Field Dictionary with definitions of commonly used fields, and an Event Taxonomy, which is a controlled vocabulary of event tags to enable a consistent identification and classification of event types.
The CEE Profile consists of three reusable components:
- Event Taxonomy — provides a listing of Event Tags that can be used to classify and identify events. The taxonomy supports common event categorization methods and identification of records that pertain to similar types of events.
- Field Dictionary — a listing of event record fields and field value types used to represent common event data. Selected fields and value types become associated with properties of a specific event instance.
- CEE Event Schema — defines the structure of an event record, including the minimum set of required fields. Event Extensions provide a mechanism for capturing additional data about an event. Users and developers can define their own event structures and customize various extensions by extending the CEE Event Schema to define their own Event Profiles.
Events
CEE Log Syntax (CLS)
The CEE Common Log Syntax directs how CEE Events are represented. Each CEE Event can be represented using one or more syntactical encodings. These encodings are well-defined syntaxes that CEE event producers can write and CEE event consumers will process.
Records
CEE Log Transport (CLT)
The CEE Log Transport provides the technical support necessary for a secure and reliable event logging infrastructure. The CEE log transport provides support for international string encodings, secure logging services, standardized event interfaces, and verifiable record logs.
CEE Architecture
Community
CEE is industry-endorsed through the CEE Board, which includes members from major operating systems vendors, commercial information security tool vendors, academia, government agencies, and research institutions.
Page Last Updated: May 15, 2013